Choosing the right fire hydrant type is a critical decision for any commercial or industrial project. Whether you’re managing a hospital, factory, warehouse, or security facility, understanding the difference between wet barrel and dry barrel hydrants ensures your fire protection system meets safety standards and operates reliably when needed.
This guide explains both types of fire hydrants, compares their specifications, and helps you determine which option suits your project in Egypt’s unique climate and regulatory environment.
What Is a Wet Barrel Fire Hydrant?
A wet barrel fire hydrant is a type of outdoor firefighting equipment where water is always present in the vertical barrel. The hydrant remains pressurized with water up to the level of each discharge outlet.
Key fire hydrant components include the bonnet (top cap), barrel (vertical pipe), stem (control mechanism), outlet nozzles, and operating nut for valve control.
Each outlet on a wet barrel hydrant has its own valve. Firefighters open the hydrant valve at the specific outlet they need, allowing water to flow immediately without operating a main valve underground.
This design makes wet barrel hydrants simple to operate and maintain. They are commonly used in regions where freezing temperatures are not a concern, making them ideal for warm climates like Egypt. Wet barrel hydrants are typically installed in urban areas, industrial facilities, and commercial complexes where quick access to water and ease of use are priorities.
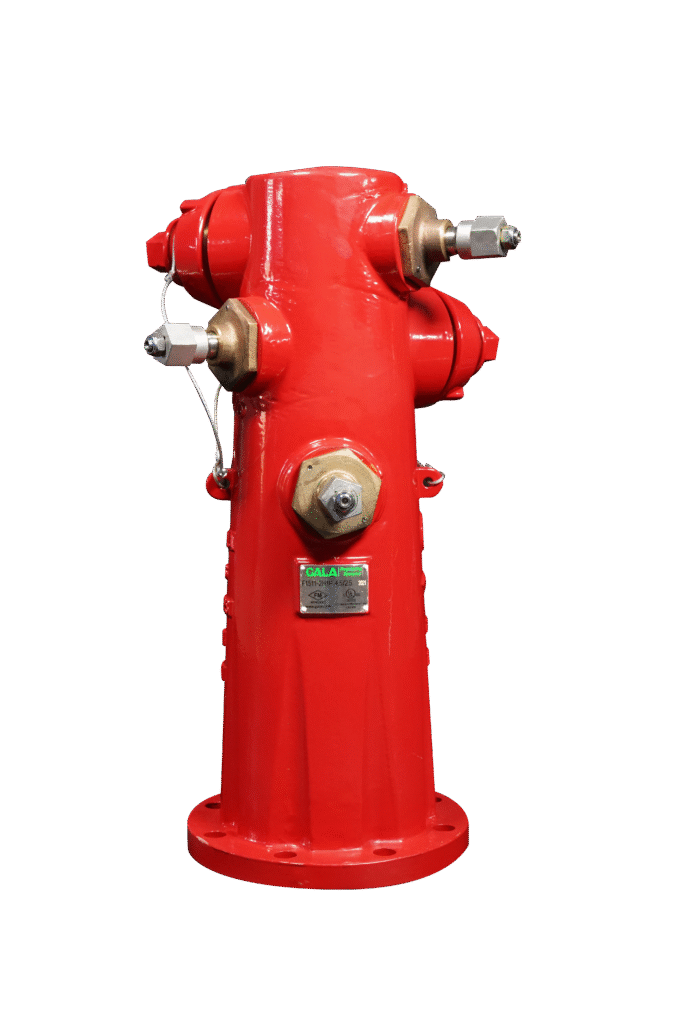
What Is a Dry Barrel Fire Hydrant?
A dry barrel fire hydrant keeps the vertical barrel empty of water when not in use. Water is stored below ground level, beneath the frost line, and only enters the barrel when the hydrant is activated.
The main valve controlling water flow is located underground. When a firefighter operates the hydrant, the valve opens and allows water to rise into the barrel and flow through the outlets.
After use, the hydrant drains automatically to prevent water from freezing inside the barrel during cold weather. This makes dry barrel hydrants essential in regions with freezing winters. Dry barrel fire hydrants are more complex in design and require more maintenance than wet barrel models.
Fire Hydrant Flow Rates and Pressure Specifications
Understanding fire hydrant flow rates is essential for proper fire protection system design. Flow capacity determines how effectively a hydrant can supply water during an emergency response.
Fire hydrants are classified by their flow rate capacity measured in gallons per minute (GPM). Standard fire hydrant flow rates include 500 GPM, 1000 GPM, and 1500+ GPM, depending on project requirements.
Operating pressure for both wet and dry barrel hydrants typically ranges from 50 to 150 PSI. Fire hydrant pressure must be maintained at least at 20 PSI residual pressure during flow testing to meet NFPA standards.
Hospital and industrial projects often require higher flow capacity hydrants (1000-1500 GPM) to protect larger buildings and critical infrastructure. Warehouses and commercial facilities may use 500-1000 GPM units depending on building size and fire code requirements.
Understanding Fire Hydrant Color Codes
Fire hydrant color coding indicates flow capacity, helping firefighters quickly identify suitable water sources during emergencies.
The standard fire hydrant color system follows NFPA guidelines:
- Red indicates flow rates under 500 GPM, a limited capacity suitable for small structures.
- Orange marks hydrants rated 500-999 GPM, adequate for most commercial buildings.
- Green identifies 1000-1499 GPM capacity, preferred for industrial facilities and hospitals.
- Blue designates 1500+ GPM flow, high-capacity units for large-scale fire protection.
While color-coding standards exist internationally, Egypt’s fire protection installations follow local fire code requirements. Habikon ensures proper fire hydrant specifications and markings for all project types.
Wet Barrel vs Dry Barrel Hydrants: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Wet Barrel Hydrant | Dry Barrel Hydrant |
| Water Location | Always in the barrel | Below ground, barrel stays dry |
| Valve Location | Individual valves on each outlet | Single main valve underground |
| Climate Suitability | Warm climates only | Cold climates with freezing risk |
| Ease of Operation | Very easy, open the outlet valve | Requires operating the underground valve |
| Maintenance | Simpler, fewer moving parts | More complex, underground valve access is needed |
| Installation Cost | Lower | Higher due to complexity |
| Flow Capacity | 500-1500+ GPM | 500-1500+ GPM |
| Typical Use in Egypt | Common and preferred | Rare, not climate-appropriate |
This comparison shows that climate is the primary factor in choosing between fire hydrant types. For projects in Egypt, wet barrel hydrants offer practical advantages in cost, hydrant valve operation, and maintenance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wet Barrel Hydrants
Advantages:
- Ease of use: Firefighters can operate individual outlets without accessing underground valves, speeding up emergency response.
- Furthermore, lower installation cost: Simpler design means fewer fire hydrant components and reduced labor during installation.
- Easier maintenance: Above-ground valves are accessible for inspection and repair without excavation.
- Climate compatibility: Ideal for warm regions like Egypt, where freezing is not a risk.
Disadvantages
- Freezing risk: Water in the barrel can freeze in cold climates, making the hydrant inoperable. This is not a concern in Egypt.
- Limited geographic use: Not suitable for regions with winter temperatures below freezing.
- Potential for leaks: Each outlet valve is a potential leak point if not maintained properly.
For hospitals, factories, warehouses, and commercial facilities in Egypt, wet barrel hydrants provide a reliable and cost-effective fire protection solution.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dry Barrel Hydrants
Advantages
- Freeze protection: The barrel remains dry, preventing ice formation in cold weather.
- Additionally, versatile use: Suitable for any climate, including regions with harsh winters.
- Code compliance: Required by fire codes in cold-climate regions.
- Automatic drainage: Water drains from the barrel after use, reducing freeze risk and stagnant water issues.
Disadvantages
- Higher cost: More complex design increases material and installation expenses.
- Difficult operation: Firefighters must operate the underground valve, which takes more time and effort.
- Complex maintenance: Underground valve access requires excavation, increasing maintenance difficulty and cost.
- Unnecessary in warm climates: The freeze protection feature offers no benefit in Egypt, making it an overengineered and costly choice.
Which Hydrant Type Is Best for You?
Selecting the right fire hydrant type depends on four key factors:
- Climate
Egypt’s warm, dry climate eliminates the need for freeze protection. Wet barrel hydrants are the logical choice for nearly all projects.
- Budget
Wet barrel hydrants cost less to purchase, install, and maintain. If budget efficiency matters, they offer clear financial advantages.
- Maintenance capacity
Wet barrel hydrants require simpler fire hydrant maintenance with accessible above-ground valves. Facilities with limited maintenance resources benefit from this design.
- Project type
For hospitals, banks, factories, warehouses, clubs, and security facilities in Egypt, wet barrel hydrants meet fire code requirements while providing reliable performance.
Real-World Application in Egypt
For example, a recent hospital project in Cairo required 1000 GPM wet barrel hydrants spaced every 75 meters. This configuration provided adequate fire protection coverage while minimizing installation costs and simplifying maintenance for facility staff.
Understanding the difference between wet barrel and dry barrel hydrants helps you make informed decisions aligned with your project’s needs and Egypt’s regulatory environment. Consequently, consulting with experienced fire protection professionals ensures your system is designed and installed correctly.
Installation Requirements for Wet and Dry Barrel Hydrants
Proper fire hydrant installation following NFPA standards is essential for hydrant valve operation, system performance, and code compliance. Both hydrant types require careful planning, but their installation complexity differs significantly.
Wet Barrel Hydrant Installation
Installation follows this sequence:
- Site preparation: Clear the area and mark utility locations
- Underground piping: Connect the water supply line to the hydrant base
- Hydrant mounting: Secure unit with proper anchoring
- Outlet valve installation: Install and align each valve
- Pressure testing: Verify system integrity and check for leaks
Installation is straightforward and faster than dry barrel systems, reducing labor costs and project timelines.
Dry Barrel Hydrant Installation
Dry barrel systems require additional steps:
- Deep excavation: Place main valve below frost line (36-60 inches)
- Drainage system installation: Prevent water accumulation
- Underground valve placement: Ensure future maintenance access
- Complex piping connections: More components than wet barrel systems
- System testing: Verify drainage function and valve operation
Testing involves verifying the drainage system works correctly and ensuring the main valve operates smoothly under pressure.
Compliance and Professional Installation
Fire hydrant installation in Egypt must comply with the Egyptian Fire Code and NFPA standards. Proper installation affects system reliability, insurance requirements, and legal compliance.
Habikon provides complete fire hydrant system services. Our offerings include:
- Design and engineering: Flow calculations, spacing analysis, code compliance
- Supply and procurement: Quality hydrant units meeting NFPA standards
- Professional installation: Licensed teams with electromechanical expertise
- Hydrant valve testing: Flow rate verification and pressure testing
- Ongoing maintenance: Annual inspections and repair services
- Fire protection system integration: Coordination with fire sprinkler systems, fire alarm installations, and fire pump stations for comprehensive building protection.
We manage projects across hospitals, industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and security complexes, delivering reliable fire protection systems tailored to Egypt’s climate and code requirements.
FAQs
What is the main difference between wet and dry barrel hydrants?
Wet barrel hydrants keep water in the barrel at all times with individual valves on each outlet. In contrast, dry barrel hydrants store water underground and use a single main valve below ground that controls flow to all outlets.
Which hydrant type is used in Egypt?
Wet barrel hydrants are standard in Egypt because the warm climate eliminates the need for freeze protection, making them more cost-effective and easier to maintain than dry barrel systems.
Are wet-barrel hydrants easier to operate?
Yes. Firefighters simply open the valve on the outlet they need without accessing underground components, allowing faster emergency response and simpler hydrant valve operation.
What are the standard fire hydrant flow rates?
Fire hydrant flow rates typically range from 500 GPM to over 1500 GPM. Flow capacity is indicated by color coding: red (under 500 GPM), orange (500-999 GPM), green (1000-1499 GPM), and blue (1500+ GPM).
What outlet sizes do fire hydrants have?
Standard fire hydrants feature two 2.5-inch outlets for hose connections and one 4.5-inch or 5-inch pumper outlet for fire engine connections. Outlet sizes may vary based on local fire code requirements and project specifications
Do dry barrel hydrants require more maintenance?
Yes. The underground valve and drainage system requires periodic inspection and fire hydrant maintenance, often involving excavation, which increases maintenance time and cost compared to wet barrel systems.
How often do fire hydrants need maintenance?
Fire hydrant maintenance should follow NFPA 25 standards, requiring annual inspections, flow testing every five years, and immediate repairs for any leaking valves or damaged components.
What fire codes apply to hydrant installation in Egypt?
Hydrant systems must comply with the Egyptian Fire Code and relevant NFPA standards. Professional contractors ensure installations meet all regulatory requirements for fire protection systems.
Who should install fire hydrants?
Licensed fire protection contractors with experience in hydrant systems, code compliance, and integration with overall firefighting infrastructure should handle installation to ensure safety and reliability.
